Sender Policy Framework (SPF) records are used to specify who is allowed to send email for a domain.
Historically, SPF records could be published using the SPF or TXT resource record types (see RFC 4408. This changed with RFC 7208, which specifies that SPF records must be published as TXT resource records only.
DNS Check supports monitoring both the TXT and SPF resource record types:
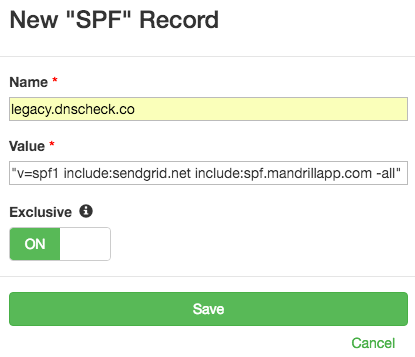
Fields
Here are the fields that make up an SPF record:
| Field | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Name | A fully qualified domain name (FQDN). | legacy.dnscheck.co. |
| Type | The DNS record type. Always set to "SPF". | SPF |
| Value | A string of text | "v=spf1 include:sendgrid.net include:windserve.com include:spf.mandrillapp.com -all" |
DNS Zone File Examples
Here's an example of how an SPF record which uses the example values from this page's Fields section looks in a DNS zone file:
; Name Type Value
legacy.dnscheck.co. SPF "v=spf1 include:sendgrid.net include:windserve.com include:spf.mandrillapp.com -all"
The Name ends in a period in the above example, so it's a fully qualified domain name.
Alternatively, you can create an SPF record that's relative to the zone file's $ORIGIN. Here's an example of how to do this using the example values from this page's Fields section:
$ORIGIN dnscheck.co.
; Name Type Value
legacy SPF "v=spf1 include:sendgrid.net include:windserve.com include:spf.mandrillapp.com -all"
Additional Resources
- RFC 7208 - defines SPF records
- SPF Introduction

Protect your DNS infrastructure with automated monitoring
Get notified immediately when DNS records change. Start monitoring your critical DNS infrastructure for free in under 5 minutes.
No credit card required • Cancel anytime